English
What are you looking for?
When it comes to precision fluid handling, gear metering pumps are indispensable tools in various industries. Ensuring their longevity and optimal performance requires a combination of regular maintenance, proper troubleshooting, and the right choice of materials. This article delves into the intricacies of gear metering pumps, offering insights and tips to extend their service life.
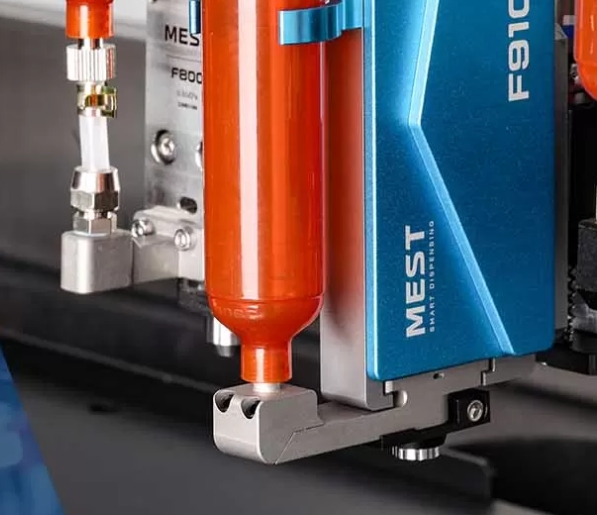
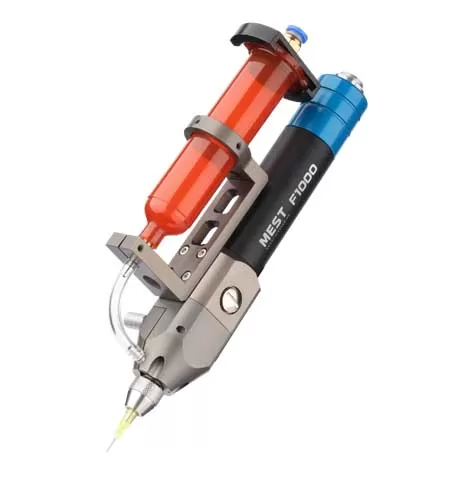
Understanding the mechanics of a gear metering pump is crucial for effective maintenance. Essentially, these pumps operate by using intermeshing gears to displace fluid. As the gears rotate, fluid is trapped in the cavities between the gear teeth and the pump casing, then transported from the inlet to the outlet. This positive displacement mechanism ensures a consistent and precise flow rate, making gear metering pumps ideal for applications requiring high accuracy.
While both gear metering pumps and positive displacement (PD) metering pumps serve similar purposes, their operational principles differ. Gear metering pumps rely on the meshing of gears to move fluid, whereas PD metering pumps use mechanisms such as diaphragms, pistons, or screws. The choice between the two depends on factors like fluid viscosity, pressure requirements, and the need for pulsation-free flow. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right pump for your specific application, thereby enhancing its lifespan.
Regular maintenance is the cornerstone of extending the life of your gear metering pump. Neglecting routine checks can lead to wear and tear, reducing efficiency and potentially causing costly downtime. Scheduled inspections, including checking for leaks, monitoring gear wear, and ensuring proper alignment, can preemptively address issues before they escalate. Moreover, regular maintenance helps in maintaining the pump’s accuracy, which is vital for applications requiring precise fluid metering.
Identifying and troubleshooting common issues can significantly enhance the longevity of your gear metering pump. Common problems include cavitation, leakage, and gear wear. Cavitation, often caused by inadequate fluid supply, can be mitigated by ensuring the pump is properly primed and the inlet conditions are optimal. Leakage, typically resulting from worn seals or gaskets, can be addressed by regular inspection and timely replacement of these components. Gear wear, which affects the pump’s efficiency, can be minimized by using the right lubricants and maintaining proper alignment.
The choice of lubricants and materials plays a pivotal role in the durability of gear metering pumps. Using high-quality, compatible lubricants reduces friction and wear, thereby extending the pump’s service life. Additionally, selecting materials that are resistant to the specific chemicals and temperatures encountered in your application can prevent premature degradation. For instance, pumps used in corrosive environments benefit from materials like stainless steel or specialized coatings that resist chemical attack.
Optimizing hot melt dispenser gear pumps for specific applications involves tailoring the pump settings and materials to the unique requirements of the task. For example, adjusting the pump speed and pressure settings can enhance performance in high-viscosity applications. Additionally, using heat-resistant materials and ensuring proper thermal management can prevent overheating, which is crucial for maintaining the pump’s efficiency and longevity in hot melt applications.
In conclusion, extending the lifespan of your gear metering pump involves a multifaceted approach that includes understanding its operation, regular maintenance, proper troubleshooting, and the right choice of materials and lubricants. By implementing these best practices, you can ensure that your gear metering pump remains reliable and efficient, providing precise fluid handling for years to come.


